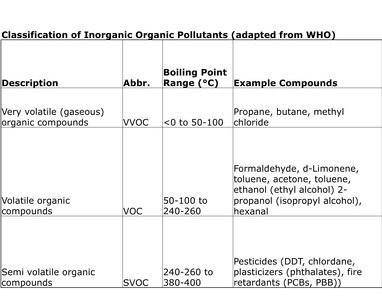
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are emitted as gases from certain solids or liquids. VOCs include a variety of chemicals, some of which may have short- and long-term adverse health effects like causing respiratory problems, some are found to increase the risk on cancer. Concentrations of many VOCs are consistently higher indoors (up to ten times higher) than outdoors. VOCs are emitted by a wide array of products. Examples include: paints and lacquers, paint strippers, cleaning supplies, pesticides, building materials and furnishings, office equipment such as copiers and printers, correction fluids and carbonless copy paper, graphics and craft materials including glues and adhesives, permanent markers, and photographic solutions.
The main concern indoors is the potential for VOCs to adversely impact the health of people that are exposed. While VOCs can also be a health concern outdoors, EPA regulates VOCs outdoors mainly because of their ability to create photochemical smog under certain conditions. EPA has no regulation yet on indoor levels, the EU is standardizing the regulations
So what to do?

Comments by our Users
Be the first to write a comment for this item.